Make an Appointment Now
info@macitbitargil.com
Acıbadem Hospitals
Make an Appointment Now
info@macitbitargil.com
Acıbadem Hospitals

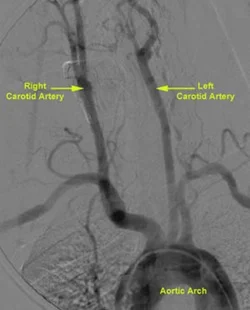
The main carotid arteries, one on each side of the neck, are also known as the “carotid artery”. The main carotid arteries consist of two main branches, called the internal and external carotid arteries, and various branches of these branches.
Internal carotid arteries, one of the main branches, are two of the 4 main vessels that deliver oxygen-rich blood to the brain. The task of the external carotid arteries is to feed the face, scalp and neck region. Carotid artery diseases occur as a result of occlusion in the carotid arteries, which have different functions in the body.
The pulse in the carotid arteries, starting from the aortic arch and running from the neck to the head, can be felt when the hands are placed on either side of the neck. Carotid arteries have an extremely important place in both the head and neck circulatory system, as they provide the transmission of oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the five and brain regions.
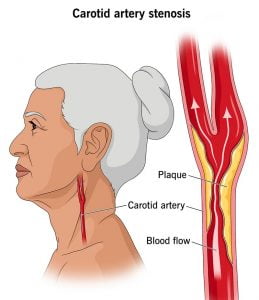
The narrowing of the inner wall that occurs as a result of the development of structures with high fat content in the inner part of the carotid arteries, which are called together with extremely important basic functions in the body, is called carotid artery disease.
Carotid artery disease, in other words carotid stenosis, can cause serious and life-threatening consequences by forming blood clots in the areas where the stenosis occurs. A blood clot that occurs in areas of carotid stenosis can cause blockage, as well as blocking a smaller artery in the brain if it ruptures, causing paralysis.
The inner walls of normal and healthy carotid arteries are flexible and smooth. There is a risk of damage to the walls of the carotid artery and carotid artery disease due to various reasons. The factors that cause the development of carotid artery diseases can be listed as follows:
In addition to these, in some cases, fibromuscular dysplasia and carotid aneurysm can also cause carotid artery disease.
Carotid artery diseases usually do not cause significant symptoms until a severe narrowing or clot formation in the artery causes an acute arterial occlusion. In this regard, although plaque formations in the carotid arteries may begin to occur in the early stages of adulthood, it may take a long time for the symptoms to appear. It is possible for symptoms to occur with an ischemic attack or stroke.
In the case of a transient ischemic attack, which resembles a stroke but is short-lived, blood flow to the brain is temporarily cut off. The symptoms of this condition, which lasts for a few minutes, disappear within an average of 1 hour and the person returns to normal. Transient ischemic attacks can also be considered as a warning that stroke and permanent brain damage may occur.
Symptoms of transient ischemic attack or stroke can be listed as follows:
Although stroke symptoms develop in the same way as transient ischemic attack symptoms, they can have different and much more serious consequences. There is a risk of permanent brain damage due to stroke. Long-term problems such as paralysis, vision and speech problems may occur, or death may occur.
Early treatment is the most important point in cases of stroke and paralysis due to carotid artery disease. There is a possibility of full recovery if the treatment required to open the occluded artery is applied within 4 hours of the appearance of these symptoms.
The first step for the diagnosis of carotid artery diseases is to evaluate the patient’s medical history and to investigate whether the person has a previous transient ischemic attack or stroke symptom.
Then the person undergoes a detailed physical and neurological examination. Carotid ultrasonography, magnetic resonance angiography, carotid angiography and computed tomography angiography tests can be applied.
Changing basic eating habits in a person’s life, maintaining ideal weight, increasing physical activity, keeping cholesterol levels within appropriate limits, and the development of high blood pressure can prevent carotid artery diseases as well as prevent their progression.
Neurologists can prescribe medication. In addition, it may be necessary to request consultation from the physicians of the relevant branches in order to control the diseases that constitute the main risk factors for carotid artery disease such as diabetes, heart disease, hypertension and obesity. Also, blood thinners and anticoagulants can be taken.
The most common surgical method in the treatment of carotid artery diseases is carotid endarterectomy. Within the scope of the relevant surgical procedure, the non-occlusive plaque in the vessel wall is removed from the vessel wall. Closure of the opened vein can be done with or without any patch.
In case of severe narrowing of the carotid artery due to atherosclerosis, also known as atherosclerosis, there is an increase in the risk of stroke due to the decrease in the amount of blood going to the brain. A stroke can occur as a result of the interruption of the clean blood supply to the brain. If blood does not reach the relevant area of the brain for more than 3 to 6 hours, there is a risk of permanent damage.
Paralysis or stroke can occur due to different reasons other than carotid artery disease. Severe stenosis or sudden occlusion in the carotid artery can lead to damage to brain functions and an increase in the risk of temporary or permanent paralysis. Since arteriosclerosis is one of the most important causes of carotid artery disease, the risk of coexistence with cardiovascular diseases is extremely high.
In the early period after carotid endarterectomy, the patient may feel tired. It is also normal to feel pain in the first 2 weeks. There may also be hoarseness.
For several weeks following treatment, activities that may cause strain, such as vigorous exercise and heavy lifting, should be avoided. During the recovery period, it is very important not to smoke and to review lifestyle habits. On the other hand, care should be taken to follow the doctor’s recommendations, not to interrupt the routine doctor’s check-ups, and to keep cholesterol and blood pressure under control.
All content on the website is for informational purposes only. Consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment methods.
2022 © All Rights reserved | Design & SEO & Development Simur Digital